
In an era where the depletion of natural resources and environmental degradation are pressing issues, the quest for sustainable development has never been more critical. One key strategy that’s been gathering momentum is the circular economy, a concept that promises to revolutionize our current linear economic model while fostering sustainability.
The linear economy operates on a ‘take-make-waste’ model, where raw materials are extracted, transformed into products, and then discarded once their use is over. However, this model has proved to be unsustainable due to the finite nature of resources and the negative impact of waste on the environment.
In contrast, the circular economy follows a ‘reduce, reuse, recycle’ approach. It aims to minimize waste and make the most of resources by creating closed-loop systems where waste is not waste but a resource. This model emphasizes product longevity, recyclability, and renewable resources, thus promoting sustainability.

The circular economy offers several benefits that directly contribute to sustainable development.
The circular economy promotes the efficient use of resources by keeping products and materials in use for as long as possible. This reduces the demand for raw materials, thereby conserving natural resources. For example, companies like Fairphone design their products to be modular and easily repairable, extending the product’s lifespan and reducing e-waste.
By minimizing waste and reliance on finite resources, the circular economy helps to decrease environmental pollution. For instance, using recycled materials in manufacturing can significantly reduce energy consumption and CO2 emissions compared to virgin materials.
The circular economy can also stimulate economic growth by creating new jobs and business opportunities. According to a study by the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, a circular economy could generate $4.5 trillion of additional economic output by 2030.
Circular practices can also bring about social benefits like improved health and quality of life. For instance, reducing waste and pollution can lead to cleaner air and water, improving public health.
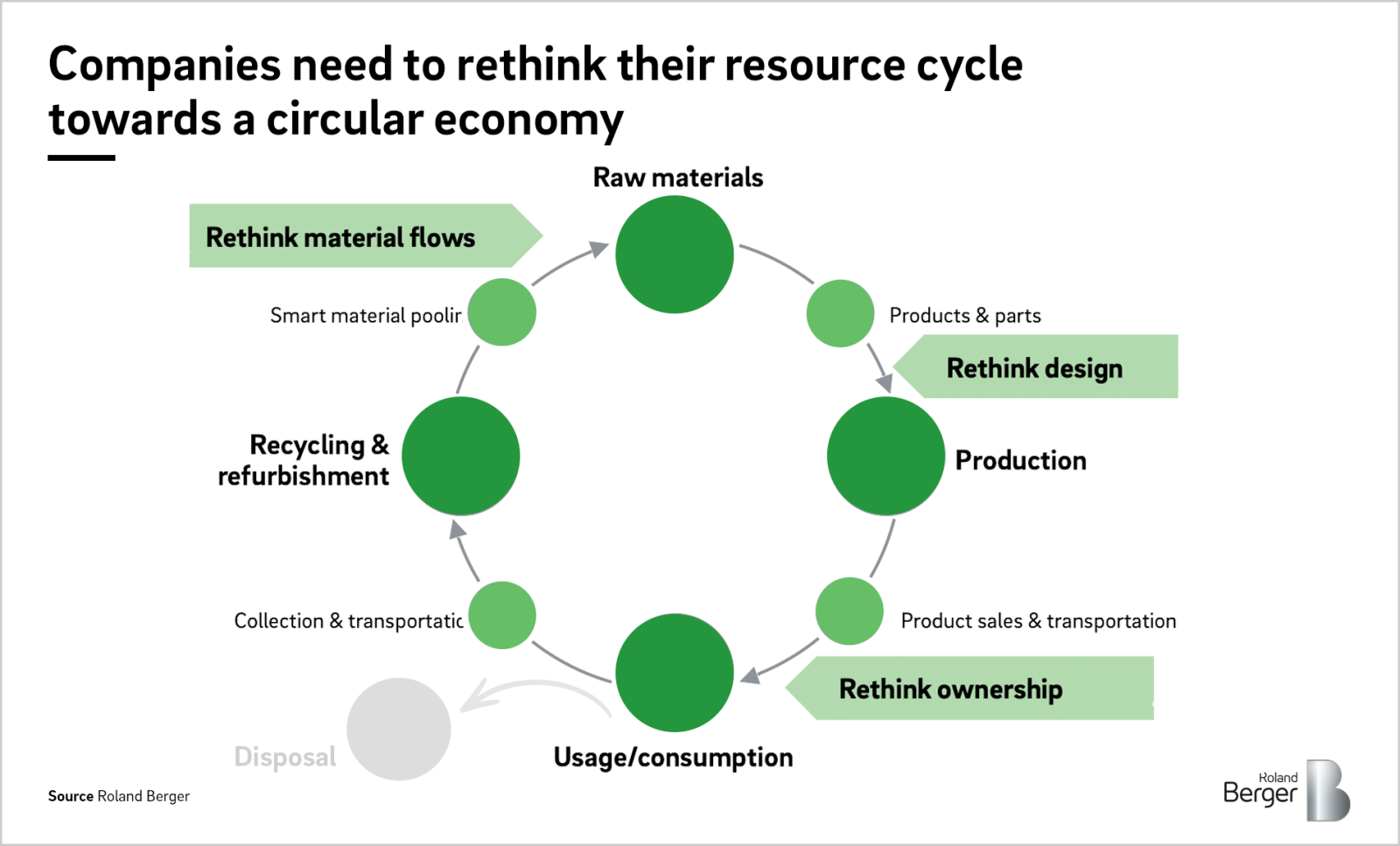
Both businesses and governments play pivotal roles in transitioning towards a circular economy. Businesses can adopt circular practices by designing products for longevity, offering product-as-a-service models, and prioritizing recycled materials in production. Governments, on the other hand, can support this transition through policies that encourage resource efficiency and waste reduction.
FAQs
1. How can individuals contribute to the circular economy?
Individuals can contribute to the circular economy by adopting sustainable consumption habits. This includes purchasing products designed for longevity, choosing services over products where possible, and recycling.
2. Are there any challenges in transitioning to a circular economy?
While the circular economy offers numerous benefits, challenges exist. These include technological constraints in recycling, the need for significant investment in new infrastructure, and the risk of job losses in certain sectors.
3. Can the circular economy completely eliminate waste?
While the circular economy aims to minimize waste, it’s unlikely to eliminate it entirely. Some waste will always be generated due to energy losses and the degradation of materials over time.
The circular economy presents a promising pathway to sustainable development by promoting resource efficiency, reducing environmental impact, and offering economic and social benefits. However, achieving this vision requires concerted efforts from businesses, governments, and individuals alike. As we look towards a sustainable future, the circular economy serves as a reminder that when it comes to resources, it’s not just about how much we use, but how we use them.
